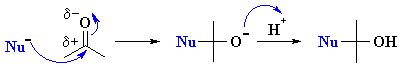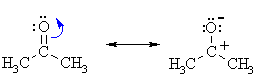 |
Chapter 17: Aldehydes
and Ketones. Nucleophilic Addition to C=O |
 |
Reactivity
Overall a simple nucleophilic addition can be represented with curly arrows
as follows:
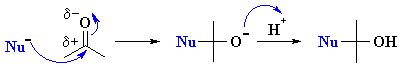
| The reactivity of aldehydes
and ketones can be easily rationalised by considering the important resonance
contributor which has charge separation with a +ve C and -ve O. |
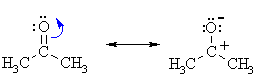 |
| QUESTION Why is this resonance
structure more important than the one with a -ve C and +ve O ? ANSWER |
|
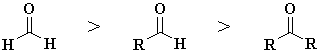
In general the
reactivity order towards nucleophiles is : aldehydes > ketones (see
below)
The substituents have two contributing factors on the reactivity at the
carbonyl C: |
- Size of the substituents
attached to the C=O. Larger groups will tend to sterically
hinder the approach of the Nu.
- The electronic effect
of the substituent. Alkyl groups are weakly electron donating so they
make the C in the carbonyl less electrophilic and therefore
less reactive towards nucleophiles.
|
 |
These trends are supported by the
trends in the equilibrium data for the formation of hydrate (see
later)
| |
Carbonyl
|
K / M-1
|
% Hydrate
|
|
Carbonyl
|
methanal
|
41
|
99.96
|
Hydrate
|
|
ethanal
|
1.8 x 10-2
|
50
|
|
2,2-dimethylpropanal
|
4.1 x 10-3
|
19
|
|
propanone
|
2.5 x 10-5
|
0.14
|
(K = [hydrate]/[C=O][H2O])