| Chapter 24: Phenols |
Cleavage of Aryl Ethers by HI or HBr
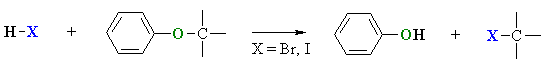
Reaction type: Nucleophilic Substitution
Summary
- Like alkyl ethers, alkyl aryl ethers, R-O-Ar, are cleaved by the strong acids HI or HBr in a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
- The products are the phenol and the appropriate alkyl halide.
- Since phenols do not react with hydrogen halides to give aryl halides, there can be no further reaction (unlike alkyl ethers and simple alcohols)
- Protonation of the ethereal oxygen creates a good leaving group, a neutral phenol molecule.
- The halide ion, bromide or iodide are both good nucleophiles.
- Depending on the structure of the alkyl group, the reaction can be SN1 or SN2 like.
- Why don't phenols react with HBr to give aryl bromides ? ANSWER
- Could a diaryl ether be easily cleaved using this method ? ANSWER
Related reactions
|
|
|
| Step 1:
An acid/base reaction. Protonation of the ether oxygen to make a better leaving group. This step is very fast and reversible. The lone pairs on the oxygen make it a Lewis base. |
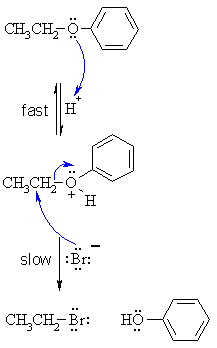 |
| Step 2:
The bromide ion functions as the nucleophile and attacks to displace the good leaving group, neutral phenol molecule, by cleaving the C-O bond. This results in the formation of an alkyl bromide and a phenol. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |