 |
These effects are a
combination of RESONANCE and INDUCTIVE
effects (see review in Ch12)
The effects are also important in other reactions and properties (e.g.
acidity of the substituted benzoic acids).
Here are some general pointers
for recognising the substituent
effects:
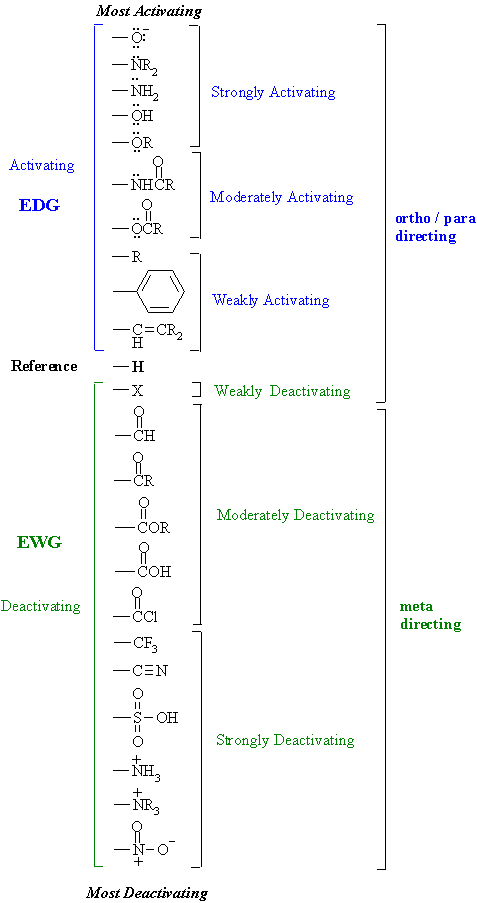
- The H atom
is the standard and is regarded as having no effect.
- Activating
groups increase the rate
- Deactivating
groups decrease the
rate
- EDG = electron
donating group
- EDG can
be recognised by lone pairs
on the atom adjacent to the p
system, eg: -OMe
- except
-R, -Ar or -vinyl
(hyperconjugation, p
electrons)
- EWG = electron
withdrawing group
- EWG can
be recognised either
by the atom adjacent to the p
system
having several bonds to more electronegative atoms, or,
having a formal +ve or d +ve charge, eg:
-CO2R, -NO2
- EDG /
activating groups direct ortho
/ para
- EWG /
deactivating groups direct meta
- except
halogens (-X) which
are deactivating BUT direct ortho
/ para
- EDG add
electron density to the p system
making it more nucleophilic
- EWG
remove electron density from
the p
system making it less nucleophilic
|
