| Useful Concepts |
| Useful Concepts |
Substitution versus Elimination
Substitution and elimination reactions often compete with each other because it's a question of nucleophilic or basic properties.
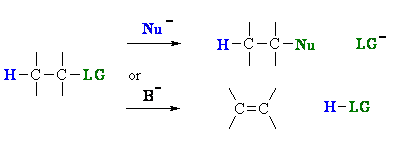
Substitution and elimination reactions are strongly influenced
by many experimental factors. Some of more important factors are outlined in the following
table.
In the table, the significance of the effect is stated first, and then the "system" that will favour
the reaction is stated.
This should help you deal with the questions....
1. When does an anion function as a Nu and when does it function as a B ?, and
therefore,
2. When to I get substitution and when do I get elimination ?
| Reaction | Solvent |
Nu or Base |
Leaving Group |
Substrate |
Example conditions |
SN1 |
Very Strong Polar solvents |
Weak Good Nu and weak base |
Strong Good LG |
Strong 3o or resonance stabilised |
alkyl halide / AgNO3 / aq. EtOH alcohol / HX |
SN2 |
Strong Polar aprotic solvents |
Strong Good Nu and weak base |
Strong Good LG |
Strong methyl or 1o |
alkyl halide / NaI / acetone alcohol / SOCl2 or PX3 |
E1 |
Very Strong Polar solvents |
Weak Weak base |
Strong Good LG |
Strong 3o or resonance stabilised |
alkyl halide / H2O alcohol / H2SO4 / heat |
E2 |
Strong Polar aprotic solvents |
Strong Poor Nu and strong base |
Strong Good LG |
Strong 3o |
alkyl halide / KOH / heat |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |