| Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols and Thiols |
| Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols and Thiols |
Reductions of Aldehydes
and Ketones
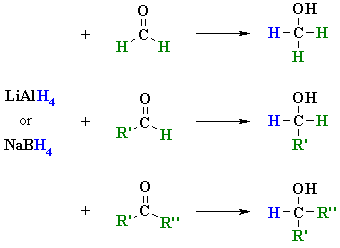
Reactions usually in Et2O or THF followed by H3O+
work-ups
Reaction type: Nucleophilic Addition
Summary
|
|
|
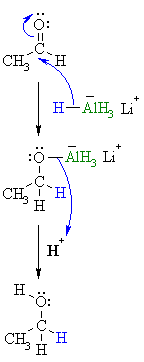
| Step 1:
The nucleophilic H in the hydride reagent adds to the electrophilic C in the polar carbonyl group in the aldehyde, electrons from the C=O move to the O creating an intermediate metal alkoxide complex. (note that all 4 of the H atoms can react) |
|
| Step 2:
This is the work-up step, a simple acid/base reaction. Protonation of the alkoxide oxygen creates the primary alcohol product from the intermediate complex. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |