| Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols and Thiols |
| Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols and Thiols |
Williamson Ether Synthesis
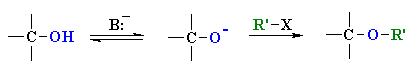
Reaction type: Nucleophilic Substitution (SN2)
Summary
Related Reactions
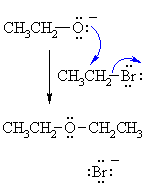
| MECHANISM
OF THE WILLIAMSON ETHER SYNTHESIS |
|
| The alkoxide functions as the nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic C of the alkyl halide displacing the bromide and creating the new C-O bond. This is an example of an SN2 reaction. |
 |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |