| Qu 1: |
(a) iv is not observed. Hydrogen bonds involve H
atoms interacting with two heteroatoms that are electronegative, most commonly
this will be O and N atoms. |
|
(b) Hydrogen bonding occurs to the amino acid 4 residues away. |
|
|
| Qu 2: |
Disulfides are formed by the oxidative coupling of thiols. Methionine
is a methyl thioether, not a thiol. Of the 20 common α-amino
acids, only cysteine is a thiol. |
|
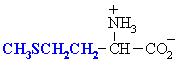 |
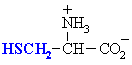 |
| methionine, a methyl thioether |
cysteine, a thiol |
|
|
|
| Qu 3: |
(a) It would be difficult to remove just the amide of the protecting
groups without destroying the amide bonds in the peptide backbone that
you have worked so hard to create. |
|
(b) Esters are usually quite easy to prepare and since esters
are more reactive than amides (review
?), so they can be easily removed without destroying the amide bonds in
the peptide backbone. |
|
(c) (1) easy and efficient to put on (2) stable to
the required reaction conditions and (3) easy and efficiently removed. |
|
|
| Qu 4: |
|
|
|
Parallel β-sheets mean
that the two C-termini are at the same end of the sheet so the amide bonds
are all in the same direction as opposed to antiparallel where the
two C-termini are at opposite ends of the sheet so the amide bonds are
opposite directions. The direction of the sheets are shown in the
JMOL diagram of the protein thioredoxin to the left by the arrow heads
on the yellow regions that represents the β-sheets.
This example contains both parallel and antiparallel arrangements of the
adjacent β-sheets. |
|