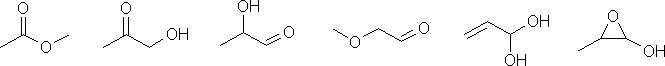
a.
Elemental
analysis : Since the % don't add up to 100% and there is no other suggestion
of any other element being present, assume the lost % are oxygen.
The molecular formula = C3H6O2
b. Index of hydrogen deficiencies = IHD = 1
c. The pKa of about 5 suggests a carboxylic acid, so that suggests CH3CH2CO2H
d. Possible functional groups that could be included are aldehydes, ketones, alkenes, ethers, alcohols and cycloalkanes.
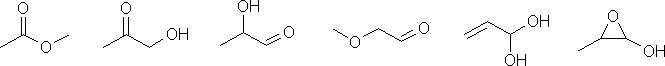
e. Two possible pairs of diastereomers are shown below. Diastereomers are a type of stereoisomer. In order to have diastereomers, you need a stereocenter. This could be a C=C or a chirality center. Of C=C then you need to draw E/Z isomers. With chirality centers, you are going to need at least two in order to draw say the (R,R) and (R,S) pair.

f.
![]()
g. IUPAC name = (1R,2S)-cyclopropane-1,2-diol
Common errors:
General: Breaking valence rules (too many bonds, incorrect charges etc.). Incorrect structural representations such as when using line diagrams or being inconsistent when showing H atoms (i.e. showing some but not all)
a . Could not do elemental analysis calculations.... did not know to assume missing percent is oxygen or making errors due to rounding.
c. Could not draw a carboxylic acid functional group correctly
e and f : not showing stereochemistry in the stereosiomers... use wedge/dash or similar diagrams that show the 3D information. Not understanding what a chirality center is or what a meso compound is.
g. Did not include R/S stereochemical designations