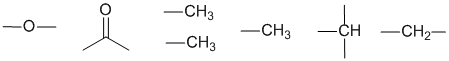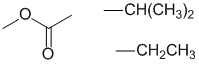Part 8: SPECTROSCOPY
The following data is available from the
question.
Note
: Remember to cross
reference things to confirm.... e.g.
IR may show C=C, use NMR to
confirm that etc.
MS: M+
seen at 116 g/mol. No isotope patterns for Cl or Br.
IR:
There is a strong absorption at about 1738 cm-1 which is probably C=O (note that's a little high for a ketone) and maybe at 1200 cm-1 which is probably C-O. There are no other absorptions of note.... no OH, NH, C=C, C≡C or C≡N
13C NMR:
The proton decoupled spectrum shows a total of 5 peaks indicating 5 types of
C. By analysis of the chemical shifts, we have a peak at 173 ppm (C=O in the carboxylic acid derivative range), at 68 ppm (maybe a deshielded sp3C) and then 3 peaks between 10-30 ppm that are
most likely from an sp3 hydrocarbon portion.
1H NMR:
The proton spectrum shows a total of 4 sets of peaks indicating 4 types of H. The peaks at about 1.15 ppm are very close together, but the expansion provides the necessary clarity.
|
d/ppm
|
multiplicity
|
integration
|
Inference
|
| 4.98 |
septet |
1 |
CH coupled to 6H, deshielded |
|
2.29
|
q
|
2
|
CH2 coupled to 3H, slightly deshielded |
| 1.16 |
d
|
6
|
6H most likely 2x CH3 coupled to 1H |
|
1.12
|
t
|
3
|
CH3 coupled to 2H
|
(q = quartet, t = triplet, d = doublet, s = singlet)
The most significant structural information
from this are:
- adding integrals shows 12H (or a multiple thereof)
- there are coupling patterns to decipher
Summary....
The MS indicated MW = 116
The IR showed the presence of C=O
13C NMR shows 5 C types including C=O that is most likely a carboxylic acid or derivative. Since there is no RCO2H in the HNMR (12 ppm) or -OH in the IR, it can not be a carboxylic acid.
H NMR gives -CH, -CH2-, -CH3, and 2 x -CH3 groups.
This information suggests a molecular formula = C6H12O
which gives MW = 100 (missing 16 = O)
Therefore, molecular formula = C6H12O2
and has an IHD = 1 consistent with the C=O.
Altogether...
|
The fragments we have are:
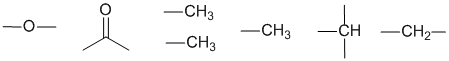
The IR, 13C and molecular formula imply that the C=O carbonyl is part of an ester.
The H-NMR 1H septet at 4.98 ppm and 6H doublet at 1.16 ppm indicate an isopropyl group, -CH(CH3)2
The H-NMR 2H quartet at 2.29 ppm and 3H triplet at 1.12 ppm indicate an ethyl group, -CH2CH3
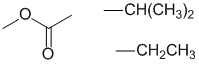
Given that H-NMR shifts of the -CH (4.98 ppm) is more deshielded than the -CH2- (2.29 ppm), it must be an isopropyl ester rather than an ethyl ester. |
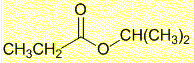
isopropyl propanoate
|
The final step should always be to check what you
have drawn. The easiest thing to check is usually the coupling patterns you
would expect to see, and the chemical shifts of each unit. You should
be asking yourself : "Does my answer give me what the H-NMR shows ?"
Common errors:
MS incorrectly read the MW for the identified M+ (check the scale). Even, no N.
IR missed the C=O
13C NMR ignored the specifics of the C=O range (i.e. subtype :173 ppm < 190 therefore it's a carboxylic acid or derivative)
H NMR had hydrocarbion pieces that did not fit the integration and coupling patterns
General
- did not check MW with data from MS
- wrong type of C=O (look at 13C NMR C=O range and check IR frequency)
- did not check HNMR chemical shifts to correct locate the alkyl groups