Part 8: MECHANISMS
Note that no other reagents are
needed in order to complete any
of these sequences, you should only be using what is there.
A
Reaction of a ketone with a 1,2-diol
alcohol to form a cyclic ketal.
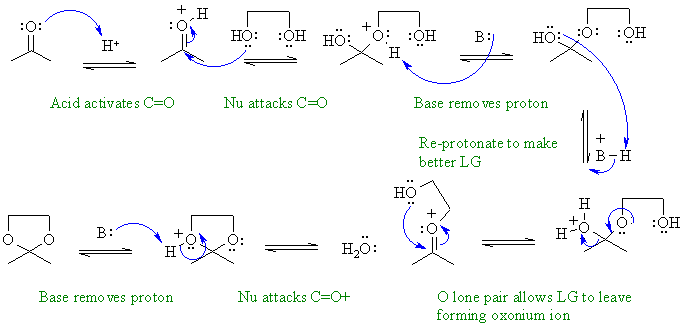
In this mechanism, B: could be C=O groups, ROH, H2O, ROR or the conjugate base of the acid catalyst.
B
Acid catalysed hydrolysis of an ester
to the parent carboxylic acid
and the corresponding alcohol. Here the benzene part has been
abbreviated
to "Ar".
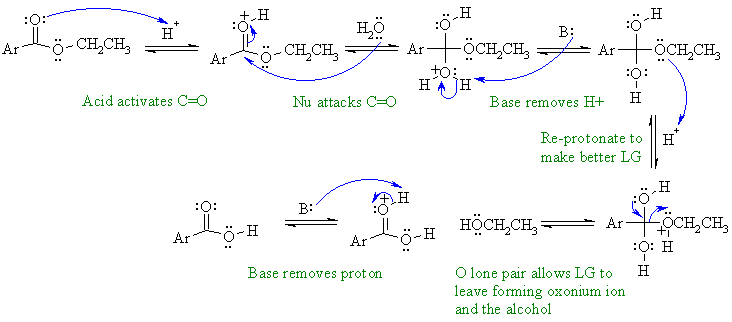
In this mechanism, B: could be C=O groups, ROH, H2O or the conjugate base of the acid catalyst.
C
Preparation of an epoxide via an
electrophilic addition to an alkene
to form a halohydrin, followed by an intramolecular nucleophilic
substitution
to give the epoxide.

In this mechanism, B: could be HO- from the hypohalous acid.
D
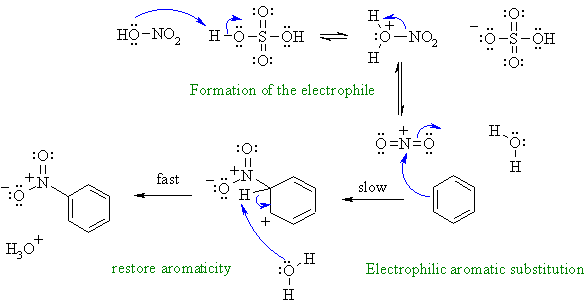
Nitration of an aromatic via an
electrophilic aromatic substitution.
First, need to show the formation of the reactive electrophile from the
nitric acid / sulfuric acid mixture.
![[Chem 350 Home]](../mol.gif) Return
to Homepage
Return
to Homepage




