Part 5: MECHANISMS
Note that no other reagents are needed in order to complete any of these sequences, you should only be using what is there.
General common errors:
(1) incorrect formal charges (2) backwards arrows (3) not showing the arrows for all the bonding changes (i.e. missing steps) (4) misuse of resonance / equilibrium arrows (5) vague arrows e.g. not starting where the electrons are i.e. on a bond or lone pair.
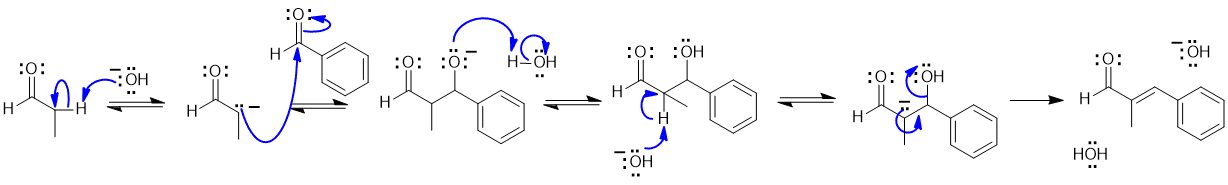
1A This is an aldol reaction (as per the Chem 353 laboratory experiment):

Common errors :
1B This is an ester hydrolysis (relates Chem 353 laboratory experiments PETE recycling & biodiesel):
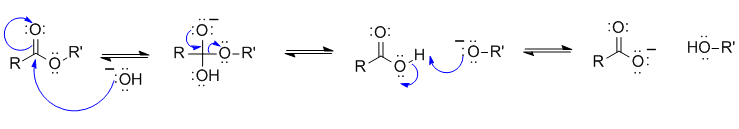
Common errors :
2A Epoxide ring opening under acidic conditions with a weak nucleophile:
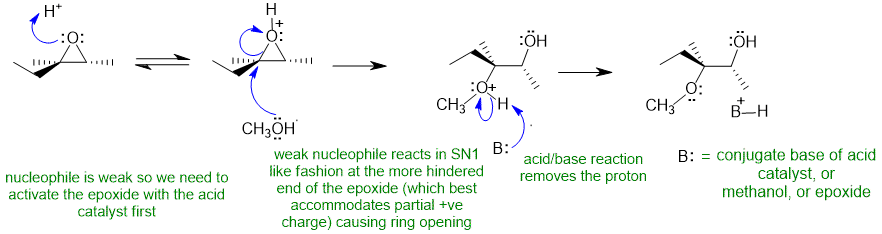
Common errors :
2B Halohydrin formation from alkene with X2 and H2O:
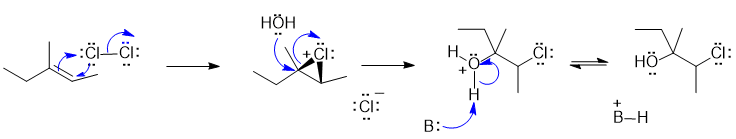
In this scheme, the base B: would be H2O
Justification: The alkene reacts with the electrophilic Cl atom to form a cyclic chloronium ion. The water molecule then attacks the most substituted end of the cyclic intermediate. The regiochemistry is controlled by the build up of positive charge on the C atom that is best able to accommodate the charge (i.e. the more stable carbocation).
Common errors: