| Chapter 13: Spectroscopy |
| Chapter 13: Spectroscopy |
Integration
The issues to understand from this page are:
What do we mean by integration ?
Integration is a mathematical term that means the area under a curve. In NMR, the curve is the spectra, and the integration is a measure of the area of the peaks in the spectra. The key thing, is that the area of the peak is proportional to the number of atoms that it represents. So in an H NMR, the integration of a peak gives the area of the peak and this area gives us a measure of the number of H atoms it represents, i.e. the number of H of that type. In many modern NMR spectra, the peaks on the spectra often look to be "lines" rather than peaks, and this tends to lead to students thinking about peak height rather than area... but it is the area that is important.
How do we measure the integration ?
There are two methods that may be encountered. First though, we should point out that the area is measured by the spectrometer itself and plotted on the spectra, we are talking about what we need to do to interpret that information:
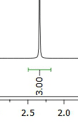
1. Numbers on spectra method (modern) The numbers are typically printed under the peak, often with a bar or two marks that represent the limits of the integration (i.e. the x axis start and end points for the area measurement). FYI : the limits are set by the person processing the spectrum. In the example to the right, the green bar shows the limits and the area = 3.00 |
 |
|
 |  |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |