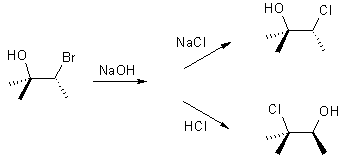| Qu 1: |
Epoxides can be
formed in two ways, either epoxidation of an alkene or via the halohydrin. |
|
(a) What is the
stereochemistry of epoxidation ? |
|
(b) If Z-2-butene
is treated with peracetic acid, what is the stereochemistry of the epoxide
?
Assign the configurations to any chiral centers. |
|
(c) If E-2-butene
is treated with peracetic acid, what is the stereochemistry of the epoxide
?
Assign the configurations to any chiral centers. |
|
(d) What is the
stereochemistry of halohydration ? |
|
(e) If Z-2-butene
is treated with HOCl then NaOH, what is the stereochemistry of the epoxide
? |
|
|
| Qu 2: |
What is the major
product from the reaction of ethylene oxide with each of the following
? |
|
| (a) H3O+ |
(b) aq. NaOH |
| (c) NaOCH3 in
CH3OH |
(d) CH3OH
with cat. H2SO4 |
| (e) LiAlH4
/ THF then acidic work-up |
(f) PhMgBr then
acidic work-up |
| (g) NaSCH3
in ether, then acidic work-up |
|
|
| Qu 3: |
What is the major
product from the reaction of propylene oxide with each of the reagents
in Qu 2 ? |
|
|
| Qu 4: |
Draw a curly arrow
mechanism to rationalise the stereochemistry of the following reactions: |
|
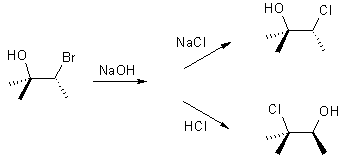 |
|
|