 |
Chapter 25: Carbohydrates
|
 |
Acetals and Ketals applied to sugars
 |
|
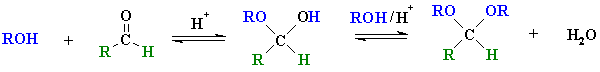
aldehyde
hemi-acetal
acetal |
|
 |
|
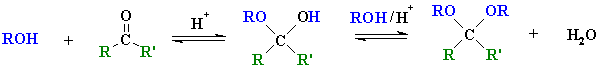
ketone
hemi-ketal
ketal |
Reaction type: Nucleophilic Addition then nucleophilic
substitution
Summary
-
Review of acetals and ketals in general
?
-
The term "acetal" used to be restricted to systems derived from
aldehydes and the term "ketal" applied to those from ketones, but
chemists now use acetal to describe both.
-
"Hemi" just means "half"- (think of hemisphere)
 |
 |
|
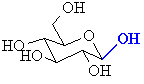
a hemi-acetal
|
an acetal
|
-
The mechanism by which aldehydes or ketones are converted to acetals or
ketals is catalysed with aqueous acid (review
?)
-
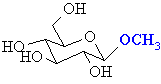
In sugar chemistry, the equilibrium is important for:
-
the interconversion of cyclic and acyclic forms of the sugar
-
the interconversion of α- and β-
anomers = mutarotation
-
the formation and cleavage of glycosides
Study Tip:
The important "piece" of an acetal or ketal is the central C
which becomes the C of the carbonyl C=O.
It can be recognised by looking for the C that is attached to two
O atoms by single bonds.
This carbon atom is the anomeric carbon or the anomeric center. |



