|
|
|
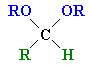
| Acetal |
The product of the reaction of an aldehyde with excess alcohol |
|
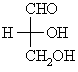
| Aldose |
A carbohydrate with an aldehyde in the open chain form. |
|
| Anomeric center |
In the cyclic sugars, the C atom
with two C-O single bonds |
|
| Anomeric effect |
A preference for polar substituents to be axial on the anomeric center |
|
| Anomers |
Two stereoisomers due to different substituent arrangement at the anomeric
center |
|
| Carbohydrate |
"carbon hydrates" = Cn(H2O)m
also referred to as sugars or saccharides |
|
| Disaccharide |
A carbohydrate composed of 2 monosaccharides units |
|
| D-sugar |
Defines the stereochemistry at a specific chirality center
relative to that of glyceraldehyde |
| Fischer projection |
A stereochemical representation commonly used for carbohydrates |
|
| Furanose |
The cyclic form of a sugar with a 5 membered ring |
|
|
|
|
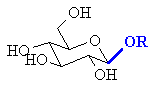
| Glycoside |
A carbohydrate where the -OH at the anomeric center has been substituted |
 |
| Glycosidic bond |
The bond that links the substituent to the anomeric center |
|
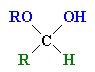
| Hemi-acetal |
The product of the reaction of an aldehyde with one equivalent of an
alcohol |
|
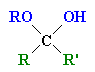
| Hemi-ketal |
The product of the reaction of a ketone with one equivalent of an alcohol |
|
| Hexoses |
Carbohydrates containing 6 C atoms |
|
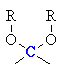
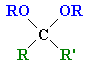
| Ketal |
The product of the reaction of a ketone with excess alcohol |
|
| Ketose |
A carbohydrate with a ketone in the open chain form. |
|
| L-sugar |
Defines the stereochemistry at a specific chirality center
relative to that of glyceraldehyde |
| Monosaccharide |
A carbohydrate with a single carbohydrate unit |
|
| Oligosaccharide |
A carbohydrate composed of a "few" (3-10) monosaccharide units |
|
| Pentoses |
Carbohydrates containing 5 C atoms |
|
| Polysaccharide |
A carbohydrate composed of a many (10+) monosaccharide units |
|
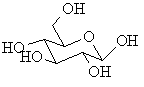
| Pyranose |
The cyclic form of a sugar with a 6 membered ring |
 |
| Saccharide |
Another word for a carbohydrate |
|
| Tetroses |
Carbohydrates containing 4 C atoms |
|
|
|
|







