| Chapter 21: Ester Enolates |
| Chapter 21: Ester Enolates |
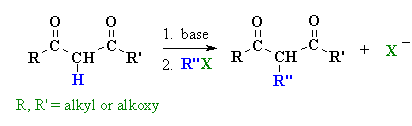
Summary
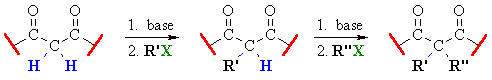
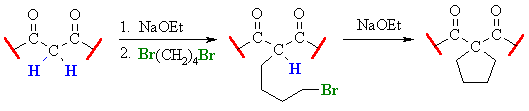
Related Reactions
|
|
|
| Step 1: First, an acid-base reaction. The ethoxide functions as a base and removes an acidic a-hydrogen from between the two carbonyl groups giving the reactive enolate. |
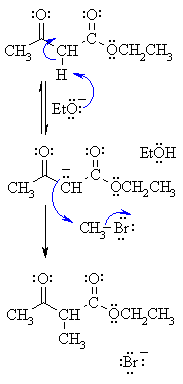 |
| Step 2: The nucleophilic enolate attacks the alkyl halide at the electrophilic carbon carrying the halogen via an SN2 type process giving the alkylation product and a bromide ion. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |