| Chapter 21: Ester Enolates |
| Chapter 21: Ester Enolates |
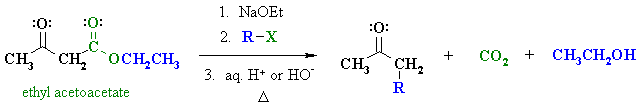
Summary
| OVERVIEW OF ACETOACETIC ESTER SYNTHESIS | |
| Step 1:
First, an acid-base reaction. Ethoxide functions as a base and removes the acidic a-hydrogen giving the reactive enolate which is then alkylated. |
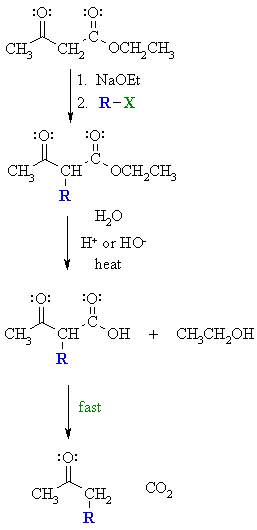 |
| Step 2: Acid or base catalysed hydrolysis of the ester to the parent carboxylic acid. |
|
| Step 3: Loss of CO2 = decarboxylation, readily occurs giving a substituted ketone. |
|
| Mechanisms for the individual steps can be found on the linked pages. | |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |